ONOS中控制器与交换机建立连接的过程
2015-04-07
控制器与交换机建立连接的过程主要分为三个阶段:控制器启动监听6633端口、交换机与控制器建立连接、控制器与交换机版本协商。
控制器启动监听6633端口
控制器启动的入口函数为
@Activate
OpenFlowControllerImpl.activate(Component context)
OSGI模块启动时候,就会调用这个函数,其中Activate注解说明了这一点:
The Activate annotation defines the method which is used to activate the component.
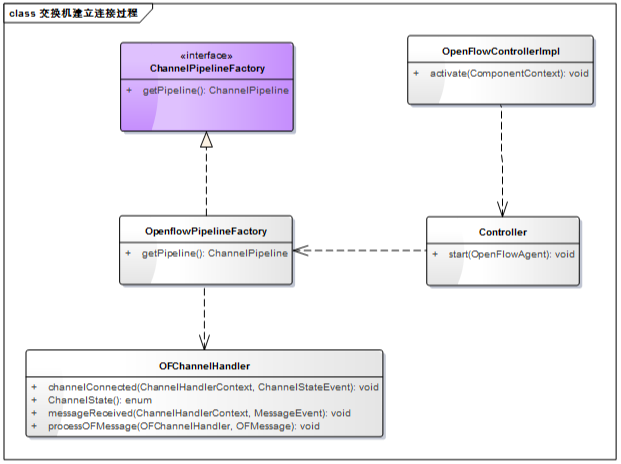
在OpenFlowControllerImpl类初始化的过程中,首先会实例化Controller和内部类OpenFlowSwitchAgent,OpenFlowSwitchAgent类十分重要,它用于跟踪已经建立连接的交换机以及它处于的状态。
private final Controller ctrl = new Controller();
protected OpenFlowSwitchAgent agent = new OpenFlowSwitchAgent();
然后启动控制器Controller.start(OpenFlowAgent agent),主要是配置参数,启动server端,监听端口,等待交换机建立连接。
public void run() {
try {
final ServerBootstrap bootstrap = createServerBootStrap();
bootstrap.setOption("reuseAddr", true);
bootstrap.setOption("child.keepAlive", true);
bootstrap.setOption("child.tcpNoDelay", true);
bootstrap.setOption("child.sendBufferSize", Controller.SEND_BUFFER_SIZE);
ChannelPipelineFactory pfact =
new OpenflowPipelineFactory(this, null);
bootstrap.setPipelineFactory(pfact);
InetSocketAddress sa = new InetSocketAddress(openFlowPort);
cg = new DefaultChannelGroup();
cg.add(bootstrap.bind(sa));
log.info("Listening for switch connections on {}", sa);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
其中cg.add(bootstrap.bind(sa));表示控制器已经启动,并且开始监听相应的端口。代码看到这里,需要有netty 的背景知识,下面将着重分析交换机连接控制器的代码。
交换机与控制器建立连接
上一段代码中比较重要的是
ChannelPipelineFactory pfact =
new OpenflowPipelineFactory(this, null);
这里将pipeline初始化为OpenFlowPipelineFactory,并且在OpenFlowPipelineFactory中重写ChannelPipelineFactory接口的getPipeline方法。
public OpenflowPipelineFactory(Controller controller,
ThreadPoolExecutor pipelineExecutor) {
super();
this.controller = controller;
this.pipelineExecutor = pipelineExecutor;
this.timer = new HashedWheelTimer();
this.idleHandler = new IdleStateHandler(timer, 20, 25, 0);
this.readTimeoutHandler = new ReadTimeoutHandler(timer, 30);
}
@Override
public ChannelPipeline getPipeline() throws Exception {
OFChannelHandler handler = new OFChannelHandler(controller);
ChannelPipeline pipeline = Channels.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast("ofmessagedecoder", new OFMessageDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("ofmessageencoder", new OFMessageEncoder());
pipeline.addLast("idle", idleHandler);
pipeline.addLast("timeout", readTimeoutHandler);
// XXX S ONOS: was 15 increased it to fix Issue #296
pipeline.addLast("handshaketimeout",
new HandshakeTimeoutHandler(handler, timer, 60));
if (pipelineExecutor != null) {
pipeline.addLast("pipelineExecutor",
new ExecutionHandler(pipelineExecutor));
}
pipeline.addLast("handler", handler);
return pipeline;
}
OpenflowPipelineFactory.getPipeline()方法作用: 为一个新的Channel创建一个新的ChannelPipeline,当一个server端的Channel接收到一个新的连接,我们会为每个新 的接受了的连接创建一个新的子Channel。这个新的子Channel使用一个新的ChannelPipeline,这个新的ChannelPipeline 由server端ChannelPipelineFactory的getPipeline创建。
在ChannelPipeline中,有idleHandler、readTimeoutHandler、HandshakeTimeoutHandler和handler这四个handler,其中 前三个handler用于超时处理,而第四个handler用于捕获这些超时产生的idleStateEvent(OFChannelHandler.channelIdle: 发送EchoRequest消息,OF心跳包)、readTimeoutException(OFChannelHandler.exceptionCaught:记录日志,关闭连接)、 HandshakeException(OFChannelHandler.exceptionCaught:记录日志,关闭连接)。
接下来分析这几个超时的设置:在初始化idleHandler的参数,this.idleHandler = new IdleStateHandler(timer, 20, 25, 0); 其中20表示读超时,意味着如果20秒内没有读到客户端发送的OF消息,则发送idleStateEvent给后面的handler处理,handler收到idleStateEvent之后,发送EchoRequest消息,这个消息是OF协议的心跳包。25表示如果25秒内没有发送OF消息给客户端,则触发同样的操作。this.readTimeoutHandler = new ReadTimeoutHandler(timer, 30);其中30表示如果30秒内没有读到OF消息,则抛出一个readTimeoutException给后面的handler处理,处理方法是断开连接。HandshakeTimeoutHandler(handler, timer, 60),其中60意味着60需要完成握手过程,否则也是断开连接。由20和30这两个数字表明:如果20秒内没有收到心跳包,则控制器发送一个心跳包,交换机返回一个心跳包,控制器必须在30秒内必须收到回包,因此这意味着一个心跳周期最多不能超过10秒。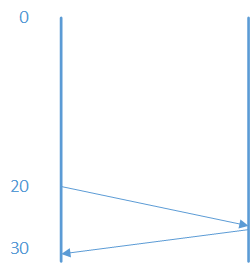
OFChannelHandler中主要关注复写SimpleChannelHandler类的channelConnected和messageReceived这两个方法,其中channelConnected用于处理Channel建立连接的ChannelStateEvent,messageReceived用于处理Channel接收到的MessageEvent。
@Override
public void channelConnected(ChannelHandlerContext ctx,
ChannelStateEvent e) throws Exception {
channel = e.getChannel();
log.info("New switch connection from {}",
channel.getRemoteAddress());
/*
hack to wait for the switch to tell us what it's
max version is. This is not spec compliant and should
be removed as soon as switches behave better.
*/
//sendHandshakeHelloMessage();
setState(ChannelState.WAIT_HELLO);
}
@Override
public void messageReceived(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MessageEvent e)
throws Exception {
if (e.getMessage() instanceof List) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<OFMessage> msglist = (List<OFMessage>) e.getMessage();
for (OFMessage ofm : msglist) {
// Do the actual packet processing
state.processOFMessage(this, ofm);
}
} else {
state.processOFMessage(this, (OFMessage) e.getMessage());
}
}
在channelConnected方法中,控制器将自身的ChannelState设置为WAIT_HELLO,意为等待交换机发送hello消息,这种代码设计模式为状态机模式。下一篇博客将详细分析ChannelState的状态机运转。接着在messageReceived方法中,对每个接收到的OF消息进行处理。到这里,交换机与控制器已经建立了TCP连接,接下来,将分析控制器和交换机握手的过程,即版本协商。
控制器与交换机进行版本协商
在ChannelState为WAIT_HELLO状态下,控制器一旦收到OF Hello的消息,便会调用processOFHello方法,在这个方法中,进行版本协商,如果协商失败,控制器则会主动断开连接。从代码中可以看出:
@Override
void processOFHello(OFChannelHandler h, OFHello m)
throws IOException {
// TODO We could check for the optional bitmap, but for now
// we are just checking the version number.
if (m.getVersion() == OFVersion.OF_13) {
log.debug("Received {} Hello from {}", m.getVersion(),
h.channel.getRemoteAddress());
h.sendHandshakeHelloMessage();
h.ofVersion = OFVersion.OF_13;
} else if (m.getVersion() == OFVersion.OF_10) {
log.debug("Received {} Hello from {} - switching to OF "
+ "version 1.0", m.getVersion(),
h.channel.getRemoteAddress());
OFHello hi =
h.factory10.buildHello()
.setXid(h.handshakeTransactionIds--)
.build();
h.channel.write(Collections.singletonList(hi));
h.ofVersion = OFVersion.OF_10;
} else {
log.error("Received Hello of version {} from switch at {}. "
+ "This controller works with OF1.0 and OF1.3 "
+ "switches. Disconnecting switch ...",
m.getVersion(), h.channel.getRemoteAddress());
h.channel.disconnect();
return;
}
h.sendHandshakeFeaturesRequestMessage();
h.setState(WAIT_FEATURES_REPLY);
}